OSTEOLOGY
OSTEOLOGY
OSTEOLOGY
Study of the anatomical structures and description of the skeleton and bones
The skeleton of the animals composed of bones and cartilages articulates and fused with the others to form the main body axis, and acts as a levers tor muscles movements and protects some soft body organs ( Brain, Heart and Lungs).
The skeleton divided into three parts
1- Axial Skeleton; includes skull, vertebral column, Ribs and sternurn .
2- Appendicular skeleton; the bones of hind and Core limbs.
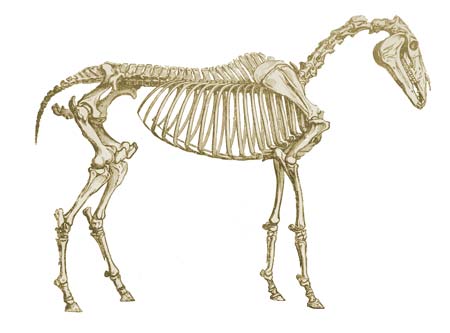 |
3- Visceral (Splanchnic) skeleton; includes some special bones that founds on the soft tissue organs such as
Types of bones:
The bones classified according to their forms and functions into four types:
1-Long bones: The bones distended in one direction, contains marrow cavity , founds in the limbs and forms strong staddle to hold the body. The typical long bone forms from cylindrical body and two articulated extremities (Femur and Humer )
2-Flat bones; These bones distended in two dimensions to prepare a wide surfaces for muscles attachment( Ex. scapulae ) or protect soft organ ( skull) these bones founds on the proximal ends of limbs ( shoulder and pelvic griddles) and skull .
3-Short bones: Similar in their dimensions, forms the tarsal and carpal bones their articular surfaces allowed the movements and protects the joint from the shocks , this type includes another bones termed sesamoid bones which lies on the articular capsules .
4-Irregular bones; Paired, median multiprocesses bones to the joins of muscles and tendon forms the vertebrae and cranium base
Bone structure
 |
The skeletal bones composed of special tissue termed Osseous tissue and consist of two parts;
A-Compact substance: Forms the outer bone cortex ,consist of fused and coalesces osteocytes.to reinforce the bone for body muscles tightening and tendons
B-Spongy substance; Brittle tissue, weak relatively ,lies under the compact tissue and forms the short and irregular bones mass, and the diphysis of long bones. the spongy substance composed of a slices of bony trabeculae to form a network of marrow spaces filled by marrow.


0 Comments
Post a Comment